Pizza Statistics: Trends, Insights, and Market Dynamics in 2024
Share
Pizza, often hailed as one of the world’s most beloved foods, has a storied history and a massive global presence. From its origins in Naples, Italy, to becoming a culinary staple in households and restaurants worldwide, the pizza industry has experienced significant growth and evolution. This article delves deep into the world of pizza through a statistical lens, providing key insights into its market dynamics, consumer preferences, and economic impact.
Pizza Statistics at a Glance
- Global Pizza Market Value (2023): $145 billion
- Projected Growth Rate (CAGR) through 2028: 5.5%
- North America’s Share of Global Pizza Market: 40%
- Average Pizza Consumption in the U.S.: 46 slices per person per year (equivalent to 23 pounds of pizza)
- Most Popular Pizza Topping in the U.S.: Pepperoni (favored by 36% of consumers)
- Percentage of Online Orders for Pizza in the U.S. (2023): Over 60%
- U.S. Pizza Industry Employment: Over 1.1 million people
- Standard Slice of Cheese Pizza: Approximately 285 calories
Global Pizza Market Overview
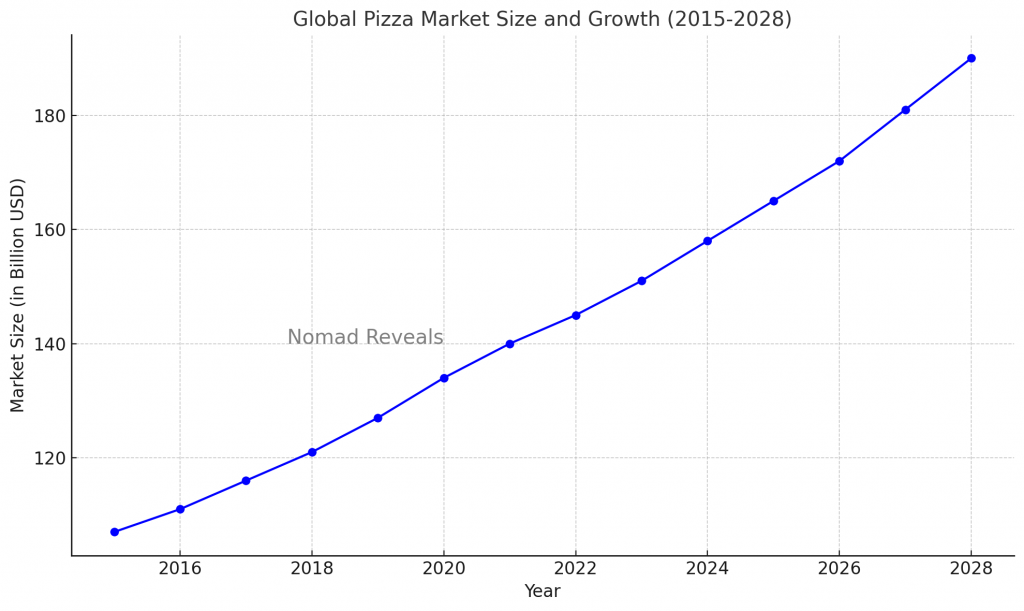
Market Size and Growth
The global pizza market has seen robust growth over the past decade, driven by changing consumer preferences, increasing urbanization, and the rise of fast food culture. As of 2023, the global pizza market was valued at approximately $145 billion and is expected to continue growing at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 5.5% through 2028. This growth is fueled by the expansion of quick-service restaurants (QSRs), innovative menu offerings, and the increasing popularity of online food delivery services.
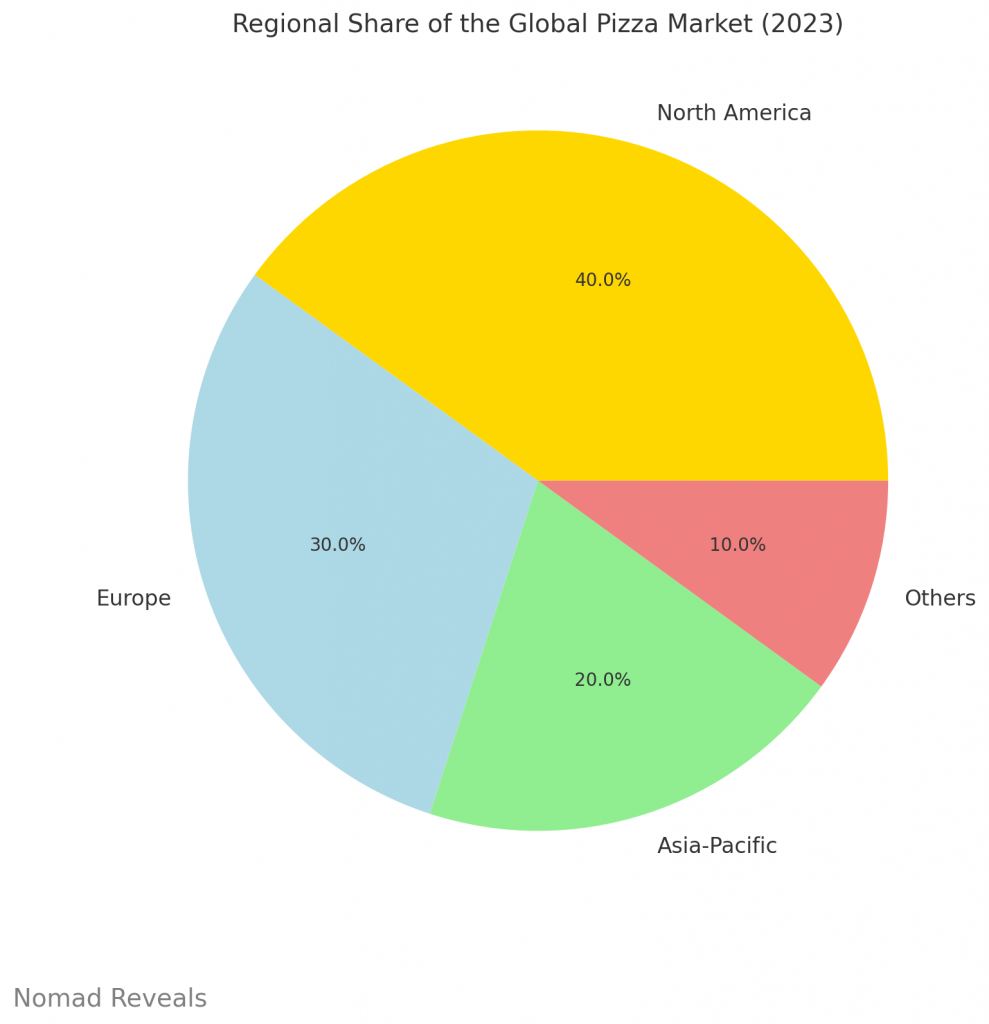
North America, particularly the United States, holds the largest share of the global pizza market, accounting for nearly 40% of the total market revenue. Europe follows closely, with significant contributions from countries like Italy, the United Kingdom, and Germany. The Asia-Pacific region, though historically less dominant in the pizza market, has seen rapid growth, particularly in countries like India, China, and Japan, where Western food culture is becoming increasingly popular.
Sources: MarketDataForecast, Statista, MordIntelligence
Pizza Consumption Patterns
In the United States, pizza consumption is exceptionally high. The average American consumes approximately 46 slices of pizza per year, equating to about 23 pounds of pizza. This translates to about 3 billion pizzas sold annually in the U.S. alone, with the majority being purchased from QSRs such as Domino’s, Pizza Hut, and Papa John’s.
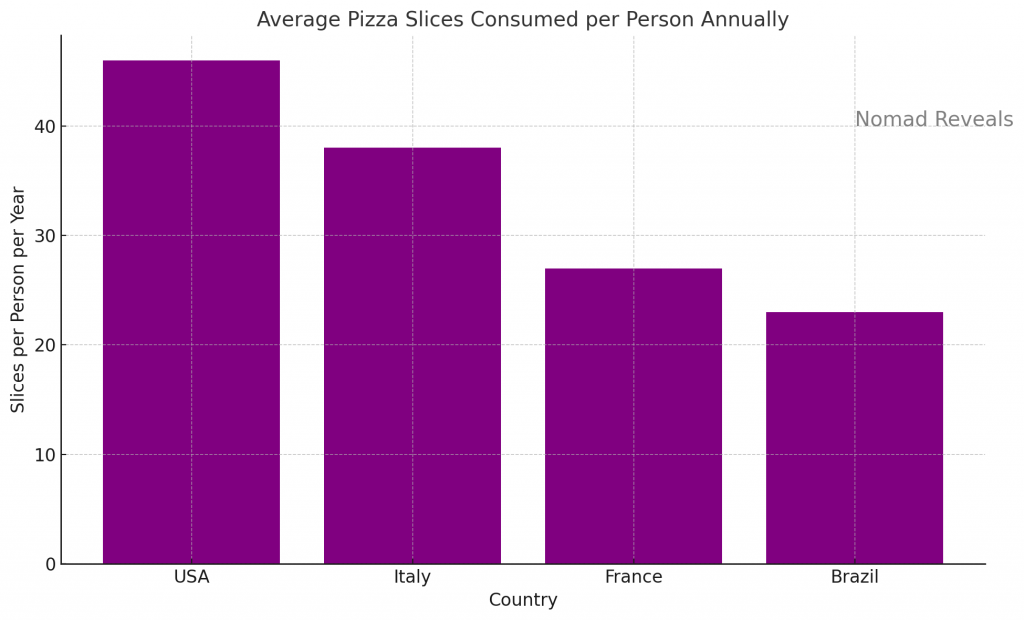
The popularity of pizza is not confined to the U.S.; countries like Italy, France, and Brazil also show significant pizza consumption. Italy, the birthplace of pizza, consumes about 7.6 kilograms of pizza per person annually, a testament to the dish’s deep-rooted cultural significance.
Sources: Businessinsider, NPD, Statista
Consumer Preferences and Trends
Popular Pizza Toppings
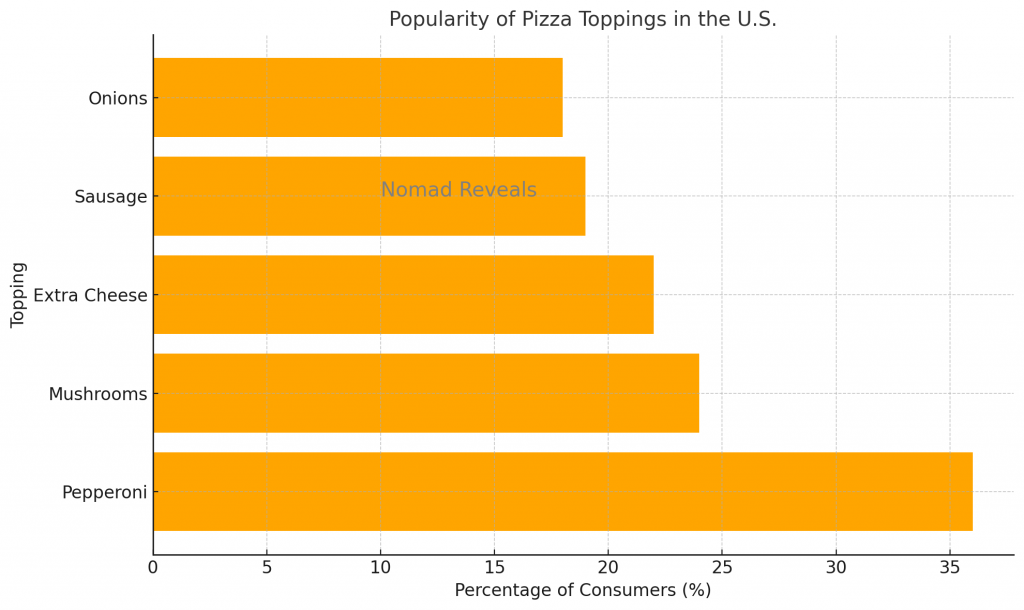
Consumer preferences for pizza toppings vary widely by region, reflecting cultural tastes and local ingredients. In the United States, pepperoni is the most popular pizza topping, favored by 36% of pizza consumers. Other common toppings include mushrooms, extra cheese, sausage, and onions. In contrast, European countries often prefer lighter toppings like prosciutto, arugula, and artichokes, reflecting their culinary traditions.
Interestingly, the trend toward plant-based and healthier eating has influenced pizza topping preferences globally. Plant-based toppings, including vegan cheese and meat substitutes, have gained traction, particularly among younger consumers and those with dietary restrictions. This shift has led many pizza chains and restaurants to expand their menus to include more vegetarian and vegan options.
Sources: PMQ, Eater, FoodNavigator
Pizza Crust Preferences
Crust preferences are another area where consumer tastes vary. In the U.S., traditional hand-tossed crust remains the most popular, but there’s a growing interest in alternatives such as thin crust, deep-dish, and gluten-free options. Thin crust, in particular, has gained popularity due to its lower calorie content and perceived health benefits.
In Italy, the home of pizza, the Neapolitan-style crust, characterized by its thin, soft, and chewy texture, is preferred. This style is also gaining popularity in other parts of the world, especially in upscale pizza restaurants that emphasize authentic Italian cuisine.
Impact of Technology on Pizza Ordering
The digital revolution has had a profound impact on the pizza industry, particularly in how consumers order their pizzas. As of 2023, online orders account for over 60% of all pizza sales in the United States . This shift towards digital ordering has been driven by the convenience of mobile apps, the ability to customize orders, and the rise of third-party delivery services like UberEats and DoorDash.
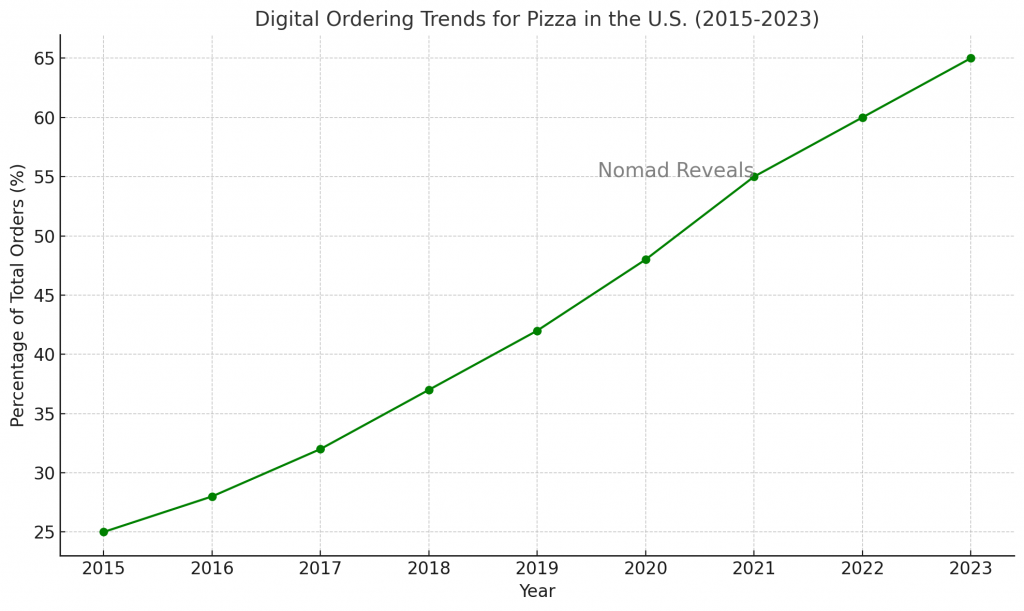
Pizza chains have also embraced technology to enhance customer experiences. Domino’s, for instance, has invested heavily in its digital infrastructure, offering features such as voice-activated ordering, GPS tracking of deliveries, and AI-powered chatbots to assist customers. These innovations have not only improved operational efficiency but have also contributed to higher customer satisfaction and increased sales.
Sources: Statista, Forbes, WSJ
Economic Impact of the Pizza Industry
Employment and Revenue Generation
The pizza industry is a significant contributor to the global economy, particularly in terms of employment and revenue generation. In the United States alone, the pizza industry employs over 1.1 million people across various roles, including food preparation, delivery, and management. The industry’s economic footprint is further expanded by its support of related sectors such as agriculture, food processing, and logistics.
Globally, the revenue generated by the pizza industry is substantial. As of 2023, pizza sales accounted for approximately 15% of the total revenue in the global fast food market. This revenue stream supports not only large pizza chains but also small, independent pizzerias, which play a crucial role in local economies, particularly in regions where pizza is a cultural staple.
Sources: IbisWorld, GrandViewResearch
Pizza Chains vs. Independent Pizzerias
The pizza market is characterized by a mix of large chains and independent pizzerias. In the United States, large chains such as Domino’s, Pizza Hut, and Papa John’s dominate the market, accounting for nearly 60% of all pizza sales. These chains benefit from economies of scale, extensive marketing campaigns, and well-established supply chains.
However, independent pizzerias continue to thrive, particularly in urban areas where consumers seek unique, artisanal pizzas that offer a departure from the standardized offerings of large chains. These independent establishments often emphasize high-quality ingredients, local sourcing, and innovative flavors, catering to a niche but growing market segment.
Sources: Statista, Restaurant Business Online
Pizza and Health: Nutritional Insights
Caloric Content and Nutritional Value
Pizza, while delicious, is often scrutinized for its nutritional content. A standard slice of cheese pizza contains approximately 285 calories, with variations depending on the type of crust, toppings, and serving size. Given that an average pizza contains 8 slices, consuming an entire pizza can easily exceed the recommended daily caloric intake for most individuals.
The nutritional value of pizza can vary widely based on its ingredients. Traditional pizzas, particularly those made with refined flour crusts, processed meats, and high-fat cheeses, are often high in saturated fats, sodium, and calories. However, there has been a growing trend towards healthier pizzas, featuring whole-grain crusts, low-fat cheeses, and an abundance of vegetables. These options provide a more balanced nutritional profile, appealing to health-conscious consumers.
Sources: Healthline, Medical News Today
Dietary Trends and Pizza
The rise of dietary trends such as gluten-free, low-carb, and vegan diets has led to significant innovations in the pizza industry. Gluten-free pizzas, made with alternative flours such as almond or cauliflower, have become increasingly popular among individuals with celiac disease or gluten sensitivities. Similarly, low-carb pizza options, often featuring crusts made from cauliflower or zucchini, cater to those following ketogenic or low-carb diets.
Sources: Celiac, Healthline
You Might also Like




